In the field of teaching and education, lesson delivery is not just about entering the classroom and sharing knowledge spontaneously. Behind every effective classroom session lies structured preparation. Two of the most important tools teachers use in this preparation process are the Lesson Plan and the Lesson Note.
Although both terms are often used interchangeably, they have distinct meanings, purposes, and writing formats. Understanding the differences and similarities between lesson notes and lesson plans is crucial not only for teachers but also for trainee educators, education administrators, and even parents who want to appreciate the work that goes into lesson delivery.
This article provides a comprehensive, well-defined, and practical explanation of lesson notes and lesson plans, their roles, their importance, their similarities, and their differences.
What is a Lesson Plan?
A Lesson Plan is a detailed outline prepared by a teacher before a class to guide the teaching process. It is essentially the teacher’s roadmap, showing how the learning objectives for a particular subject or topic will be achieved.
Think of a lesson plan as the blueprint for the class session. Just as an architect uses a building plan to ensure a structure is erected properly, a teacher uses a lesson plan to ensure that the lesson is delivered effectively, covering objectives, content, teaching methods, and evaluation.
Key Features of a Lesson Plan
-
Objectives – Clearly states what the learners should know or be able to do at the end of the lesson.
-
Instructional Materials – Lists resources and teaching aids (e.g., charts, textbooks, multimedia).
-
Introduction – Explains how the lesson will be introduced to grab learners’ attention.
-
Presentation Steps – The step-by-step activities to be carried out during the lesson.
-
Evaluation – How learning outcomes will be assessed (questions, tests, exercises).
-
Conclusion – How the teacher will summarize and reinforce the topic.
Example of a Lesson Plan (Simple Snapshot)
-
Subject: Mathematics
-
Topic: Fractions
-
Objective: At the end of the lesson, students should be able to define fractions and solve basic fraction problems.
-
Instructional Materials: Chalkboard, fraction chart, counters.
-
Introduction: Asking students to share items like biscuits among friends.
-
Presentation: Teacher explains fractions, uses diagrams, solves examples.
-
Evaluation: Teacher asks students to solve fraction problems on the board.
-
Conclusion: Summarizes definition and practical examples.
What is a Lesson Note?
A Lesson Note is the teacher’s detailed written explanation of the content to be taught in class. While the lesson plan acts like a guide or framework, the lesson note is the full script that contains the detailed body of the lesson.
It is usually written after the lesson plan and expands on the points stated in the plan. Lesson notes are often more detailed because they are meant not only to guide the teacher but also to be a reference for school authorities, supervisors, or even other teachers who may use them.
Key Features of a Lesson Note
-
Topic and Subject – States the subject and lesson title.
-
Class and Duration – Specifies the class (e.g., Primary 4, SS2) and how long the lesson lasts.
-
Objectives – Similar to lesson plan objectives but written in measurable terms.
-
Previous Knowledge – Connects the new topic with what learners already know.
-
Content Development – The bulk of the lesson, usually in detailed written form with explanations, examples, and activities.
-
Teacher’s and Learners’ Activities – Specifies what the teacher will do and what students are expected to do at each stage.
-
Conclusion and Evaluation – Reinforces the lesson and tests knowledge gained.
Example of a Lesson Note (Simple Snapshot)
-
Subject: Basic Science
-
Topic: The Solar System
-
Class: JSS1
-
Duration: 40 minutes
-
Objectives: By the end of the lesson, students should be able to:
-
List the planets in the solar system.
-
Explain the order of the planets.
-
Identify key features of each planet.
-
-
Previous Knowledge: Students have learned about the Earth and its environment.
-
Content Development:
-
Explanation of the solar system.
-
Description of the planets and their order.
-
Activities: Students recite planets in order, draw diagrams.
-
-
Evaluation: Teacher asks students to mention planets and their order.
-
Conclusion: Recap of the solar system with emphasis on key points.
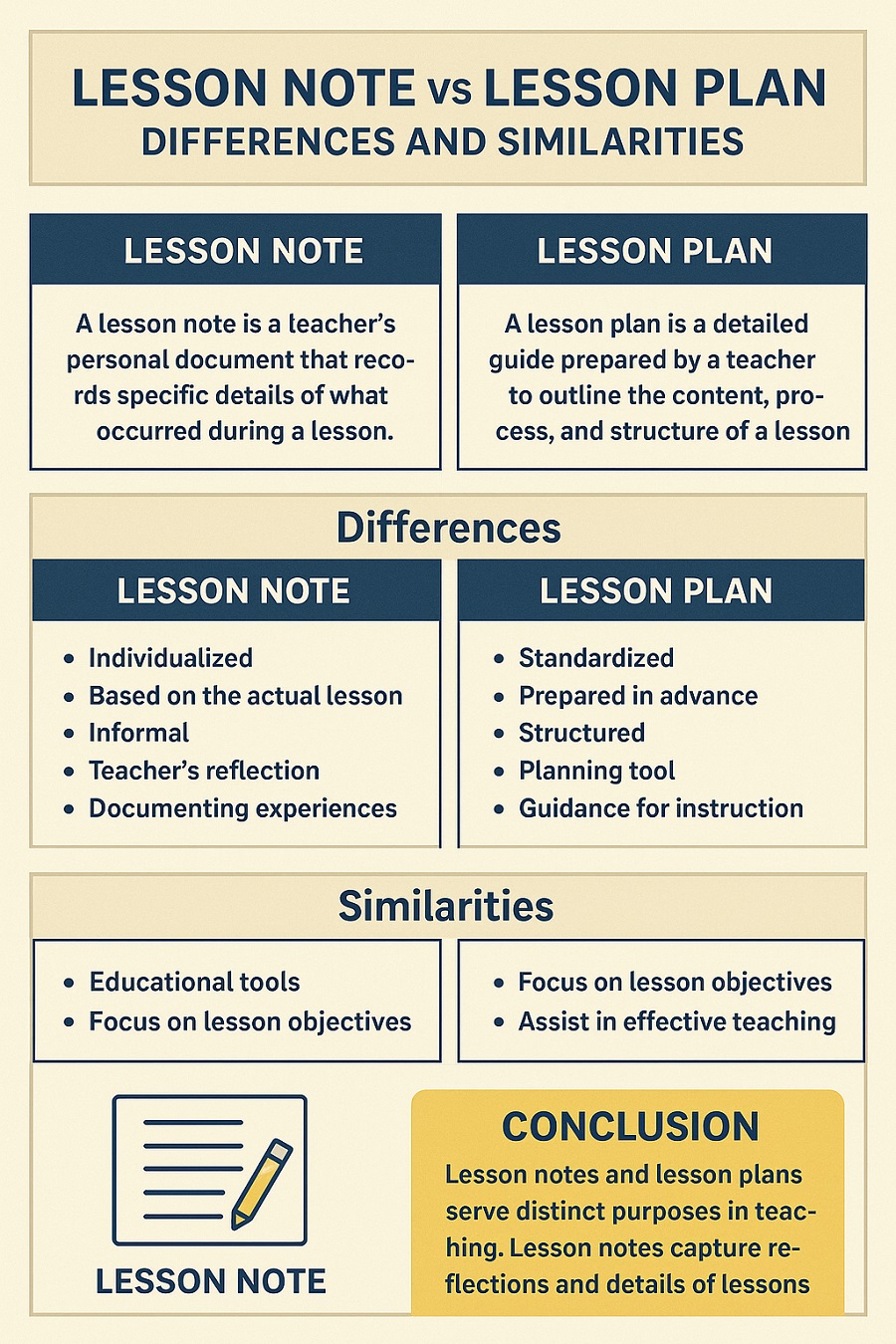
Lesson Note vs Lesson Plan: Key Differences
While both serve as essential tools in teaching, they differ in scope, purpose, and detail.
| Feature | Lesson Plan | Lesson Note |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A structured outline of how a lesson will be taught. | A detailed written explanation of the lesson content. |
| Purpose | Guides the teacher in delivering the lesson. | Provides the full content and activities of the lesson. |
| Format | Concise, point-form outline. | Detailed narrative, often more elaborate. |
| Audience | Primarily for the teacher. | For teacher, school, supervisors, or colleagues. |
| Content | Objectives, materials, steps, evaluation. | Objectives, content, teacher/learner activities, notes. |
| Detail Level | Short, summarized. | Detailed, explanatory. |
| Preparation Order | Written first as a framework. | Written after the lesson plan, expands details. |
Similarities Between Lesson Notes and Lesson Plans
Despite their differences, both tools share some similarities:
-
Purpose of Guidance – Both aim to guide the teacher in lesson delivery.
-
Focus on Objectives – Both state what the learners should achieve at the end of the lesson.
-
Preparation Tools – Both are prepared before class.
-
Evaluation Component – Both include methods to check whether learners have understood the lesson.
-
Support Effective Teaching – Both contribute to structured and effective classroom delivery.
Why Are Lesson Plans and Lesson Notes Important?
-
Promote Organization – They prevent the teacher from going off-topic.
-
Ensure Learning Objectives – They guarantee that intended outcomes are met.
-
Help With Supervision – Supervisors and principals use lesson notes to assess teaching quality.
-
Boost Teacher Confidence – Prepared teachers are more confident and effective.
-
Support Substitute Teachers – Another teacher can use a lesson note if the main teacher is unavailable.